
Ah, science. Sure, it does plenty of amazing things for society: finding treatments for cancer, putting people in space. But along the way, scientists also discover some truly bizarre things about the way the world works. From DNA-devouring worms to M&M-crazed bees, here are some of the strangest science stories of the year.
1. Hold the sex, pass the DNA
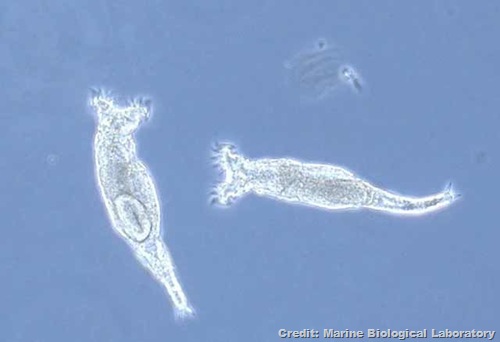 A pair of bdelloids probably don't get excited about each other as two humans in such close proximity might. Bdelloids don't need sex to reproduce. A pair of bdelloids probably don't get excited about each other as two humans in such close proximity might. Bdelloids don't need sex to reproduce. |
Sure, birds do it, bees do it, but rotifer worms don't bother. Having sex is a key way for species to increase their genetic diversity and prevent the build-up of harmful genetic mutations. But an all-female worm called the bdelloid rotifer seems to have kept its kind alive for 80 million years without engaging in sex. Instead of cozying up to a fellow rotifer, the creature devours fungi and bacteria and incorporates some of that DNA into its own genetic code. The DNA meals may provide a healthy dose of antioxidants, the researchers propose.
2. Colourful honey
Hives of sugar-crazed bees in France are turning chocolate M&Ms into colourful honey. The bees got hooked on the candy because a biogas plant in the region processed waste from a local Mars Chocolate Factory. The bees collected the sugar in their storage stomachs and then transferred it to other bees in the colony. The artificial colouring in the candy dyed the honey striking shades of blue and green.
3. Mother-child brain meld
 Research showing for the first time that foetal DNA can migrate into the brain of its mother suggest mama will always have a bit of her baby on her mind. Research showing for the first time that foetal DNA can migrate into the brain of its mother suggest mama will always have a bit of her baby on her mind. |
And you thought pregnancy hijacked the brain. New research revealed that foetal cells migrate to a woman's brain, where they can linger for decades. The scientists found traces of male sex chromosome DNA in the cadavers of women as old as 94. While scientists don't understand exactly what these cells do, some theorize they may help the woman's body repair tissue and may even play a role in Alzheimer's disease.
4. Living longer with a snip
 A eunuch carrying a weapon keeps an eye on a harem in Tunis, Tunisia, 1931. New research on Korean court eunuchs suggests these castrated men may get a lifespan boost. A eunuch carrying a weapon keeps an eye on a harem in Tunis, Tunisia, 1931. New research on Korean court eunuchs suggests these castrated men may get a lifespan boost. |
File this under life-prolonging treatments few would want to try. Until 1894, some Koreans had their testicles removed in order to rise in a traditional court hierarchy and get invited to exclusive sleepover parties at the royal palace. The Korean eunuchs lived up to 20 years longer than their intact male counterparts. Though it's not clear exactly why this happened, the male sex hormone, testosterone, is known to suppress the immune system and worsen heart health. [Extending Life: 7 Ways to Live Past 100]
5. Fossil forests return
 An ancient forest once flourished on the Canadian Arctic's Bylot Island (shown here), and researchers say global warming may revive it. An ancient forest once flourished on the Canadian Arctic's Bylot Island (shown here), and researchers say global warming may revive it. |
One unforeseen side effect of global warming: Ancient fossilized Arctic forests may come back to life, according to one study. With temperatures across the globe rising fast, these forests, which lived about 2.5 million years ago, may soon revive. The forests grew when the annual temperature was around freezing, or 32 degrees Fahrenheit (0 degrees C). The current average yearly temperature in the Arctic is 5 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 15 degrees C), but if the climate warms significantly, grandchildren of people living today may be able to visit newly revived Arctic forests.
6. Cockroach to the rescue
Remote control cockroach
Cockroaches: They can go where no man can and are impervious to the most hostile conditions. Now scientists have turned those bugs into features by creating remote-controlled cyborg cockroaches that could scurry into disaster areas to look for survivors. Because they are so small, the remote-controlled roaches could skitter under rubble after an earthquake.
7. Bridge to nowhere
A giant bridge of dark matter, an elusive substance that can be sensed only by its gravitational pull, lies between two massive galaxy clusters about 2.7 billion light-years from Earth. The findings support the idea that galaxy clusters form where dark matter filaments cross. The Subaru telescope in Hawaii picked out evidence of the filament in 2001, but it wasn't until this year that physicists went back and discovered the mysterious bridge.
8. Maggots ID the dead
White maggot
Just when you thought CSI couldn't get any stranger, it's now possible to identify human bodies from the maggots that eat them. Police in Mexico identified a body that was so badly burned there was no soft tissue left. The bugs harboured traces of human DNA in their intestinal tracts, allowing forensic scientists to identify the body as the remains of a girl who had been abducted several days before.
9. Baby crime fighters
 According to research conducted earlier this year, looking at a baby face activates regions of the brain associated with caregiving. Credit: Image via Shutterstock. According to research conducted earlier this year, looking at a baby face activates regions of the brain associated with caregiving. Credit: Image via Shutterstock. |
What's the best way to fight crime? Put up adorable images of chubby little babies. At least, that's the strategy a few shopkeepers are turning to in Gravesend, a rough part of London that was heavily looted in riots last year. The hope is that would-be vandals will look at the innocent little faces and find that their looting, stealing hearts are turning to mush. While it may sound silly, the idea has some basis: Previous research showed baby faces activated loving, caring circuits in the brain.
10. New human species
 A view of a skull from the Red Deer Cave People. Researchers found the species had unique features seen neither in modern nor known archaic lineages of humans. A view of a skull from the Red Deer Cave People. Researchers found the species had unique features seen neither in modern nor known archaic lineages of humans. |
Neanderthals and hobbits aren't the only species that may have coexisted with modern humans. Scientists in southwest China have discovered the bizarrely shaped skulls of a possible new human species called the Red Deer Cave People that existed until the end of the ice age, about 11,000 years ago. The odd skeletons had prominent jaws and jutting cheekbones, and middling-sized brains more commonly seen in human ancestors from hundreds of thousands of years ago.




No comments:
Post a Comment
Please adhere to proper blog etiquette when posting your comments. This blog owner will exercise his absolution discretion in allowing or rejecting any comments that are deemed seditious, defamatory, libelous, racist, vulgar, insulting, and other remarks that exhibit similar characteristics. If you insist on using anonymous comments, please write your name or other IDs at the end of your message.